Can mathematics help you cook just enough?

Leftovers are usually no issue. But what if you’re cooking for hundreds of people? Using
mathematics, specifically the Central Limit Theorem, we try to cook just the right amount.
Maximising efficiency is risky business (Part 2) - The mathematics behind logistics chains
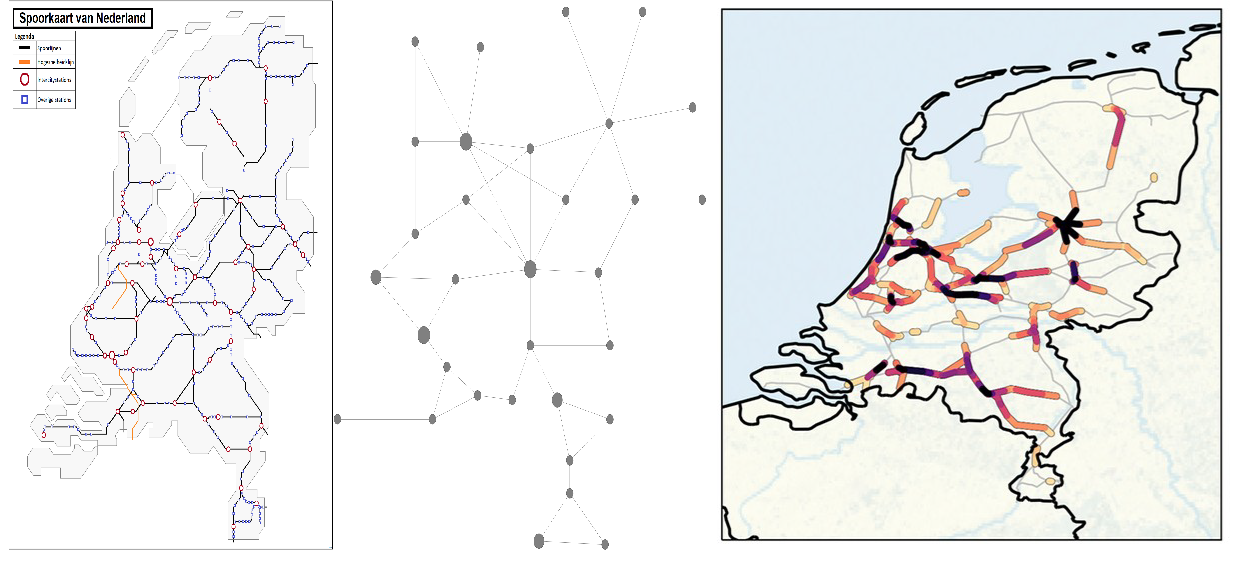
We can use mathematics and more specifically networks to study logistics chains. In the first article we described how logistic chains work. In this second part, we go one step further and dive in the mathematics.
Maximising efficiency is risky business (Part 1) - Logistics chains and cascading small delays

Think of a local car dealer selling cars in your region. To make sure new cars are delivered on time a whole mechanism involving various people, factories, and transport companies, must operate in coordination. This is a highly complex process where mathematics plays an important role.
Picking the best route for order pickers
The routes that pickers in warehouses take are essential to efficiency. But which route is best?
A peek into decision making in service systems

Often due to large waiting times customers abandon shops (online or physical), and owners don't realize that they have left. We call this a loss of opportunity. This is an important concept in queueing theory.
From building a family tree to discovering the suspect of a crime
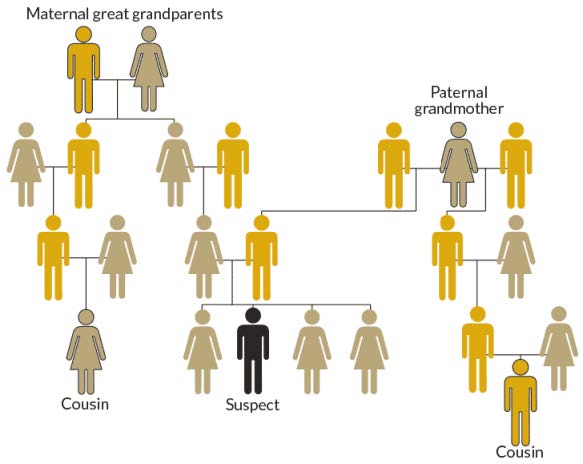
Between 1973 and 1986 multiple rapes and murders were committed in the state of California. Years later the idea was raised that these crimes might be connected. But traditional DNA analysis from the samples found at the crime scenes, could not identify the culprit.
Trust and other wonderful mistakes humans make

Trust is required when we buy a used car from a personal connection or via-via. When we vote for a politician we trust that they will act in our favour. In this article we will explore how Game Theory is used in attempts to model trust and cooperation.
Distributing work in a network of servers
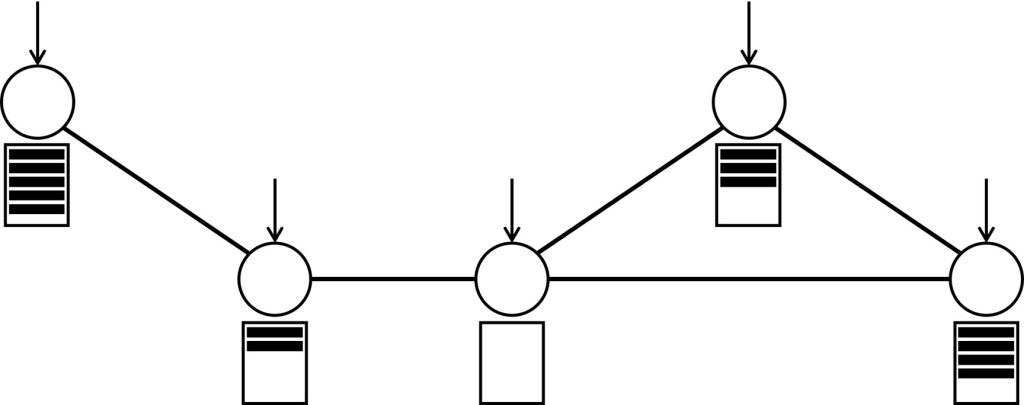
This article discusses a fun puzzle that illustrates a beautiful open problem in this area: queueing theorists are trying to figure out how the structure of a network impacts its ability to distribute work among the nodes.
Why scientists keep failing at stopping COVID and how mathematicians can help.
Despite our level of development, the pandemic has been continuously causing us struggles for two years. This gives rise to an obvious question: How can contemporary science not deal with a flu-like virus?
Let’s make it on time without wasting time on it

What if I tell you that long queues in airports are also caused by the impatient passengers that arrive too far in advance at the airport? Today, we will analyze how the organization of the security check queue affects the waiting time of passengers.
