What is the chance of throwing six with a fair die?

If, after reading the title, your immediate response is to shout "1/6-th", then you have correctly answered the question. Well done! However, in this article we will focus on the meaning of this question. What exactly is this "chance" of which you've just exclaimed it equals 1/6-th?
The Elegant Heist: Mastering the Art of Necklace Splitting

Ever wondered how stolen necklaces are tactfully divided? Join us on a captivating journey into the math under necklace splitting! This journey will lead us to a wonderful and very important theorem in mathematics, the Borsuk-Ulam theorem.
The magic of mathematics ♠️♥️♣️♦️
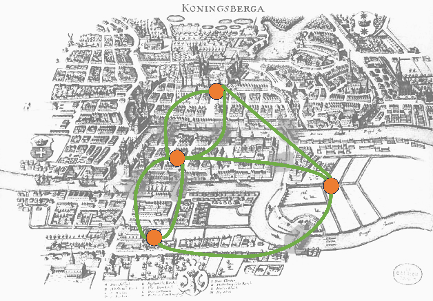
Did you know that a city tour was the foundation of the mathematical field of graph theory? And that graph theory has applications even in magic?
ICTS-NETWORKS workshop: A Confluence of Ideas

In the vibrant city of Bangalore, India, the International Centre for Theoretical Sciences (ICTS) played host to a discussion meeting titled "Challenges in Networks" from January 29 to February 2, 2024.
Does no small structure mean larger homogeneous ones?
A conjecture of Erdős and Hajnal from 1989 says that forbidding any specific substructure results in existence of a very large homogeneous one! In this article you will have a look into one of the most fascinating problems in modern graph theory.
Picking up 13 different cards from 13 piles (Part 2)
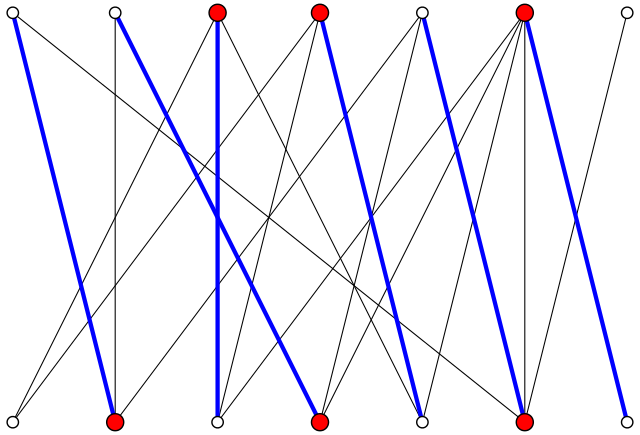
In Part 1 Jackie explained to her fried Sam how the problem of picking a card from each of the 13 piles so that there is exactly one card with each rank translates to a problem on bipartite graphs. The mathematical problem asks you to find a perfect matching in a regular bipartite graph.
Picking up 13 different cards from 13 piles (Part 1)

Did you know that if you divide a pack of cards into 13 piles of 4 cards, then you can always pick one card from each of the 13 piles so that there is exactly one card with each rank? There is some beautiful math behind this puzzle.
The 100 prisoners escape puzzle
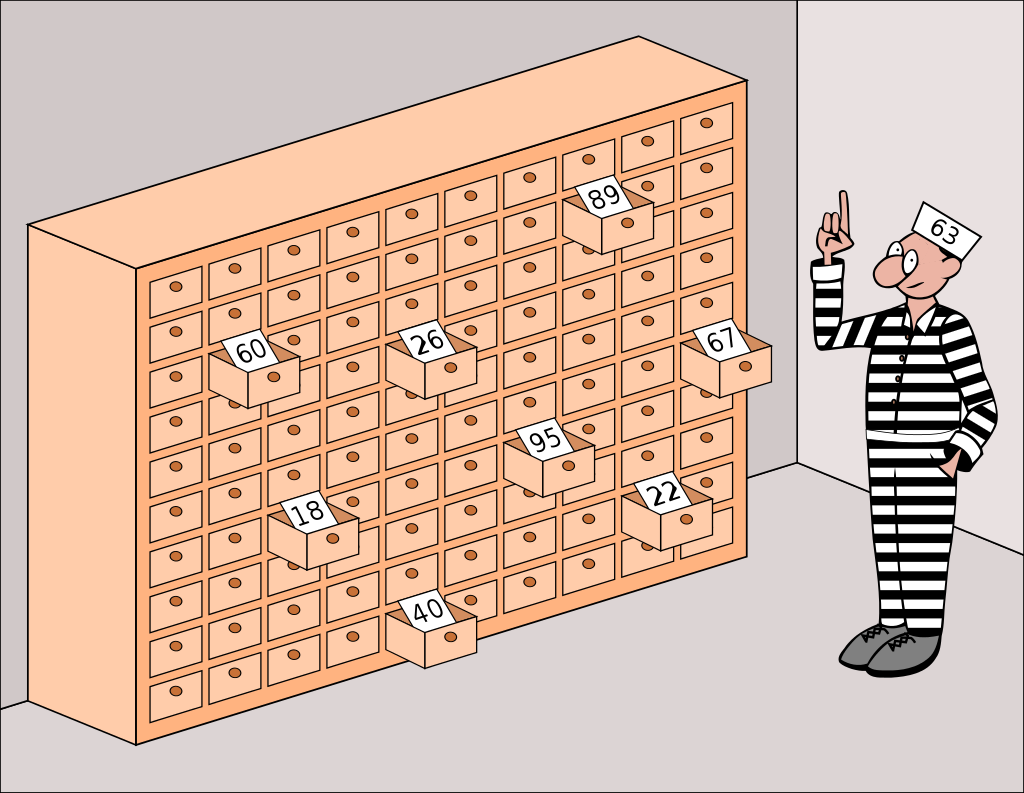
In this article, we will discuss a mathematical riddle that "seems impossible even if you know the answer". It is better known as the 100 prisoners problem.
Structure is everywhere. So is chaos.
Pick 45 numbers between 1 and 100. Try to avoid creating pairs whose difference is the square of some number and you will fail. Always.
Is a rapidly mutating virus unstoppable?
How can one hope to understand the precise structure of a virus if it is able to become unrecognizable within weeks? The mathematics behind this questions didn't let go of my mind for extensive periods of time during my PhD studies in Belgium.
