The eerie phenomenon of quantum entaglement

In this article, I will discuss the weird phenomenon called quantum entanglement, to which Albert Einstein referred as "spooky action at a distance".
How the schedule in the TATA Steel Chess Championship forced Carlsen to help Caruana win
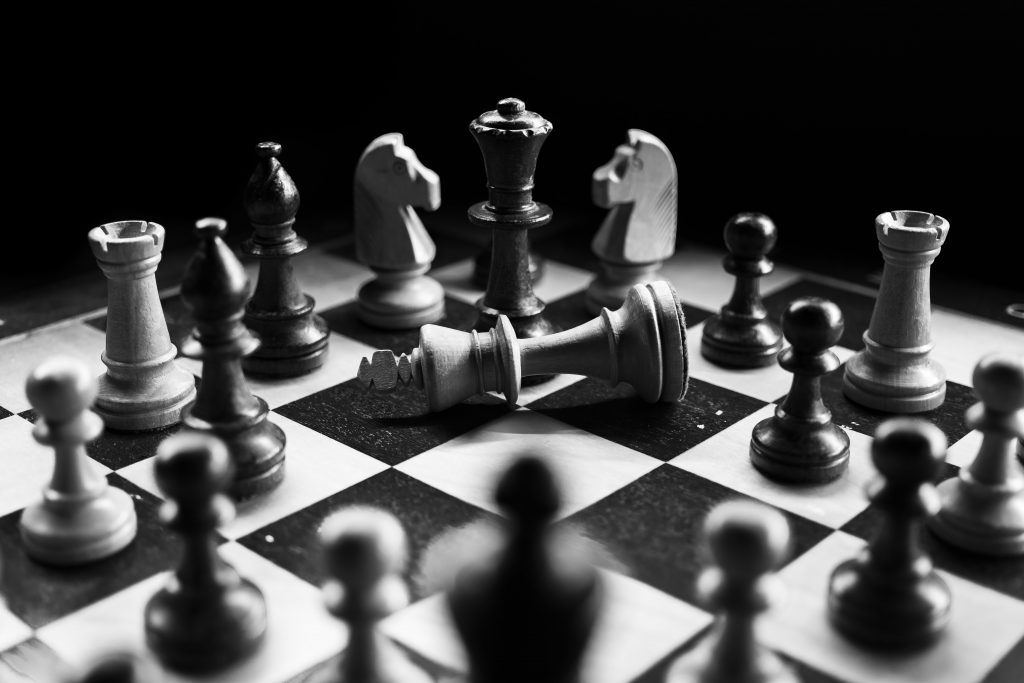

Every January, the best chess players in the world compete in the TATA Steel Chess Championship, organized in Wijk aan Zee (The Netherlands). Among this year’s fourteen participants were Magnus Carlsen, world no. 1, coming into the tournament with an unbeaten streak of 104 matches, and Fabiano Caruana, the world no. 2.
Drugs dumping in the Netherlands; a gentle introduction to uncertainty and statistics.

Most of you will agree with my girlfriend that when the number of drugs dumping increases for three years in a row, this points to an increase in the demand for drugs, the number of illegal producers, the amount of drugs produced etc. Doing some math you will see this may not be the case.
Quantum synchronization in complex networks
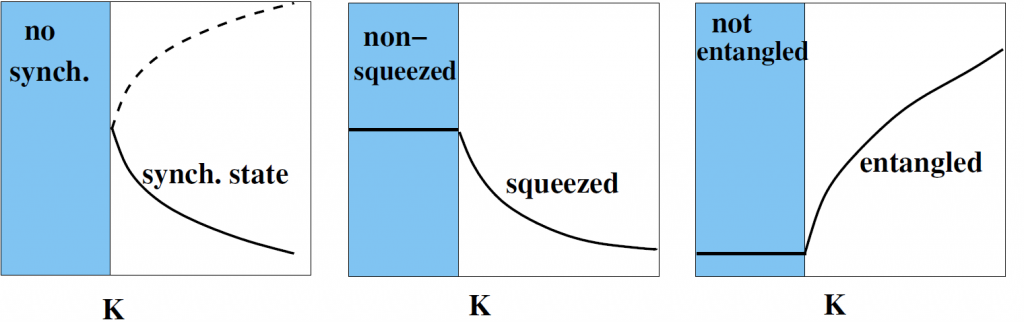
As many phenomena in the classical world have quantum counter part, it raises the question if this is also true for synchronization. As synchronization is a collective phenomenon, it may help gaining a better understanding of how collective phenomena in the classical and quantum world are connected.
Complex networks
Have you ever wondered what mathematicians mean when they talk about mathematical models of real-life phenomena? And what can such a model tell us about the network-phenomenon we are studying?
Vaccination and the friendship paradox!
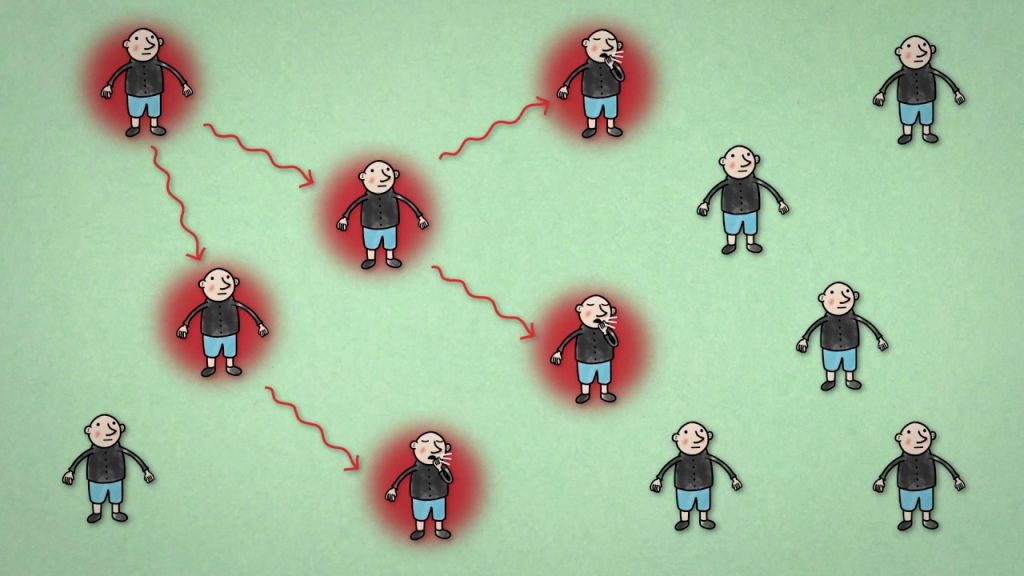
On social media it seems like everyone around me is more popular than what I am. It is a mathematical statement: the friendship paradox!
Degrees in graphs III: Which degrees sequences are possible?
Paul Erdős and Tibor Gallai developed a beautiful criterion to decide precisely when a degree sequence is graphical.
A network made of math
Alexander Grothendieck (1928—2014) is viewed by many as one of the greatest mathematicians of all time. He made contributions to many different fields, but the work he is mainly celebrated for is his shaping of some of the most abstract, fundamental branches of mathematics.
Large Deviations Theory: understanding the incredibly rare
Probability Theory is one of the most important tools for studying networks. Most things Probability Theory tries to explain are about average or typical observations.
Degrees in graphs II: Degree sequences
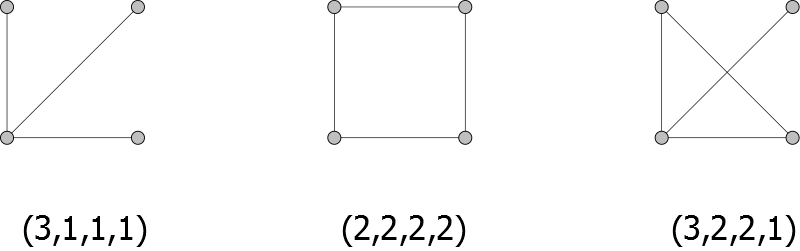
The degree sequence of a graph is the sequence of degrees of all its elements.
